Logga in

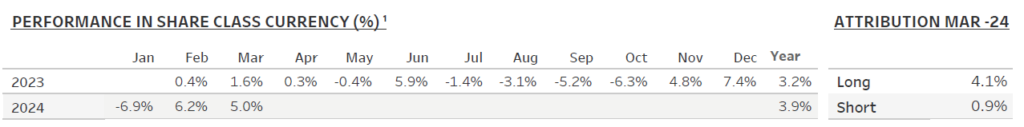

1) Share Class I SEK
Performance for other share classes towards the end of the report.
FUND MANAGER COMMENTARY
The Coeli Renewable Opportunities fund gained 5.0% net of fees and expenses in March (I USD share class). It is up 3.9% this year and has increased 7.2% since the inception on February 6, 2023.
In March, the fund outperformed the two most comparable indices, the Wilderhill New Energy Global index (NEX) and the iShares Global Clean Energy (ICLN), by 2.1% and 4.5%, respectively, taking the year-to-date outperformance to 15.1% and 14.1%. Since inception, the fund is ahead by 39% and 37%, respectively.
Like last month, the fund made a profit from both the long and the short side; longs gaining 4.1% and shorts 0.9%. Alpha generation since inception continues to be strong and in March, almost two thirds of the themes made a positive contribution. The best performer, adding 2.1% to NAV, was “US Renewable Development”, which benefitted from the increasing focus on the expected boom in demand for electricity from data centers (DC) for artificial intelligence (AI). We dig deeper into this topic later in the report.
The ‘Grid’ theme continued to grind higher, contributing 1.3% to NAV, with all six long positions adding value in March. Our largest position, Chart Industries (GTLS), rose 15% in March and is up by almost 50% since the bottom in January. The “Wind” theme also did well as Nordex (NDX1) in its fourth quarter earnings report confirmed our long-held view that both order backlog and margins are going higher. The stock is up 26% since Q4 earnings.
Dispersion in the renewable energy equity space has improved considerably over the last couple of months which generates interesting trading opportunities for the fund. March ended with a net exposure of 53% and a gross of 126%. We added a new theme called “Grid Owners” towards the end of the month.
MARKET COMMENT – BACK TO NO LANDING AND HIGHER FOR LONGER?
The S&P 500 rallied for the fifth month in a row, setting another eight all-time-high records and closing the month with a 3.1% gain. The index is up by more than 10% since the beginning of the year. At that time, the bond market was expecting inflation to continue to fall and the FED to cut rates more than six times in 2024. However, after two strong inflation reports, the market is pricing in less than the three cuts projected in the FED plot. Nevertheless, the rally is healthier than in January as it is no longer mainly about the ‘Magnificent 7’. In fact, the S&P 500 equal weight index outperformed the main index by almost 2%-points in March. Even interest rate sensitive small-caps took part in the rally as Russel 2000, the key small cap index, rose by 3.4% in March and is up almost 5% this year. The renewable indices also rose during the month, although they continue to lag the market.
In light of the recent hotter than expected inflation data and what seems like an upward trend in both monthly core CPI and super core CPI since the middle of last year, we were somewhat surprised that FED chairman Powell continues to hint that a cut in June is still likely. However, echoing our discussion from January, it is important to note that the FED believes the Non-accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) is substantially lower than in the past. This implies that only a minor uptick in unemployment may justify a reduction in interest rates. Given the FED’s dual mandate to combat both inflation and unemployment, the significance of the latter should not be underestimated in an election year. Despite a more hawkish tone from several FED governors after the FOMC press conference, we still find it likely that the rate cutting cycle starts this year, but in the meantime, we keep a relatively conservative net exposure.
RENEWABLE ENERGY - ROADBLOCKS ON THE AI HIGHWAY
The march of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is at full throttle, promising a future brimming with innovation. For some, the hope is that it will cure everything from cancer to climate change. However, the road to the intelligent future is starting to experience growth challenges. Power supply is emerging as a pivotal battleground where extremely power-hungry data centres (DCs) are sucking up available capacity where they can find it. Combined with the ongoing roll out of electric vehicles, heat pumps and the general electrification of society, the power demand of the data centres accelerate a looming undersupply of power and more importantly available grid capacity. This affects almost every industry and highlights the challenges ahead; how do we decarbonize without slowing down growth and innovation?
The energy needed for AI is rising exponentially as models get more complicated and are trained on more parameters. According to ThundersaidEnergy, an energy research consultancy, it was 4 times more energy intensive per parameter to build Chat GPT-4 which was trained on about 10 times more parameters than Chat GPT-3, resulting in approximately 40x higher energy consumption. As AI models get even more complex with ever larger data-processing volumes, the energy demand will increase exponentially. Although Thunder expects as an offset a massive improvement of 40x in computer energy performance, it recently increased its 2030 estimate for AI energy demand by 80% to as much as 900TWh. To put that into perspective, it is almost on par with the energy demand for all other internet operations. Moreover, it would account for almost 2.5% of estimated global electricity demand in 2030, up from less than 0.05% of electricity demand last year.
This is simply extraordinary growth over only a few years. Although it would put pressure on other energy intensive industries, it is a golden opportunity for renewable developers as it will drive substantial demand for renewable energy Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). One of the funds’ holdings, AES, is one of the largest suppliers of PPAs to the so called hyperscalers (the cloud service providers such as Meta, Google, Amazon, Microsoft etc). These companies are expected to account for much of the growth in large DCs and half of AES’ backlog of as of 2023 is with hyperscalers, almost twice as much as at the end of 2022.
So far, AI has not significantly moved the needle though. As it takes 2-3 years to build a large DC and even longer to build and connect new renewable energy, the DC builders have prioritized locations with readily available grid and power capacity, in some cases even connecting directly to nuclear power plants. Nuclear power offers clean, reliable energy with ample access to water for cooling, often allowing the DCs to be housed on the power plant’s premises. However, as this carbon free power is used by DCs instead of communities, gas fired power plants need to run more frequently. This is obviously a problem for tech companies which all have net zero or 100% renewable targets. However, Morgan Stanley estimates that only about 11GW of nuclear power is available for data centre, which would cover less than 10% of the 2030 demand calculated by ThunderSaid Energy. Due to the tech companies’ strong commitment to decarbonise their operations, we believe this trend will inevitably drive further growth of renewable energy.
Data centres will be built around the world, but the growth in AI demand, at least initially, is significantly stronger in the US. This is one of the reasons for our more optimistic view to US renewable developers than the European companies, as we have mentioned in previous monthlies. According to Data Center Hawk, a DC market research firm, a significant majority of global DC leases are concentrated in the United States. In 2023, the US accounted for 6GW of the total 8GW contracted globally (excluding China). See the table below for detailed figures.
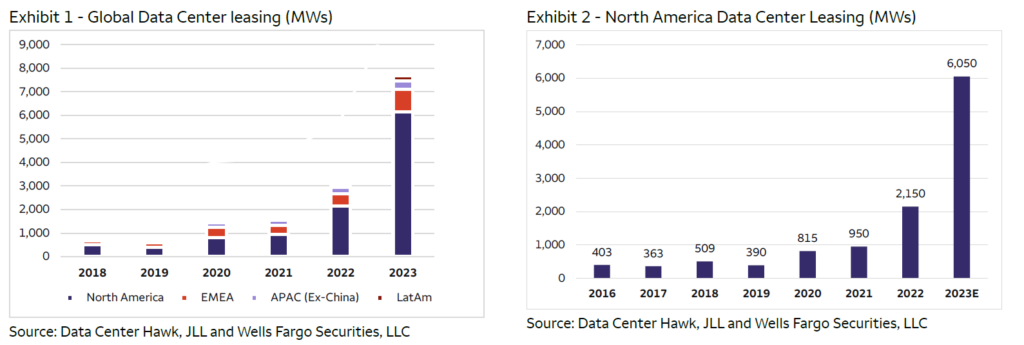
As can be derived from the data, the DC leases grew by 150% in 2023, accelerating from 100% growth in 2022. However, in the US leases increased by almost 200%.
Power is so central to data centres (DC) that they are quoted in Megawatts (MWs), not square meters. The DCs that run the learning models (LLM) are huge beasts boasting several hundred MWs each, equal to the energy demand of a small town. However, some LLM DCs parks that are being discussed are even in the 1-3GW scale. To put this in context, in 2021 the entire Stockholm region consumed the equivalent capacity of about 2.3GW.
While LLM DCs are massive, they are not latency sensitive and could be placed further from the end consumer. The “inference DCs” that run the queries however need to be placed much closer to city centres. We expect to see the growth of LLM DCs continue in areas where electricity is cheap and clean, like in the Nordic countries for instance. Unfortunately, the DCs are likely to push out other decarbonization efforts, like battery factories or green hydrogen plants. In contrast with these plants which both would need significant subsidises despite using the cheap and often land locked energy, the hyperscalers can afford to pay premiums to get access to the same energy.
Unfortunately, the build out and access to clean energy is not the only challenge. A much bigger bottleneck is the expansion of the grid for all the DCs to connect.
In the west we have for decades taken for granted that the grid has plenty of capacity, companies can easily expand and relatively quickly connect to the grid. This is changing. Even before gen AI, the shift from a fossil energy system, albeit slowly, to an electric one has brought the grid close to the breaking point in many countries. We have in several monthly reports discussed these challenges, for instance March-23 “Renewable Energy – Grid connection the next bottleneck?”. AI with its massive load demand is amplifying these problems. It might seem straightforward; we need to build out both the distribution and transmission grid. But the reality is more complicated; there are local opposition, permitting delays, strained supply chains, and, in the US, political difficulties agreeing across state borders. For example, a large transmission line across several states in the US can require up to 13,500 permits and take more than 15 years to complete. Interconnection costs have quadrupled since the year 2000 and it takes on average twice as long to connect.
Expanding and speeding up connection to the grid has become a key issue across the US, although the problem varies from state to state. For example, while the grid operator ERCOT in Texas can connect in under two years, the waiting time in Santa Clara, California is about six years. In Virginia, which is the world’s biggest DC hub, boasting 2.5GWs of DCs, the largest electric utility has announced that some new facilities will be delayed until 2026.
Despite the outsized growth in the US, the problem is not US specific. Singapore, Amsterdam, and the wider Dublin area has in recent years instituted partial or complete bans of new DC projects due to excessive energy use. In Ireland, DCs already use around 10 percent of available electricity. Even in West London, the Financial Times reported that new housing could be banned until 2035 because DCs had contracted all available interconnections.
Even before the emergence of AI, we were positive to the renewable developers, especially the ones in the US. Although the investment case is even better today, given the grid bottlenecks we continue to be even more optimistic to companies involved in expanding and improving the grid infrastructure. Since 2010, investments in renewable energy have more than doubled while global grid capex is barely changed at USD 300bn per year. This is about to change drastically as can be witnessed from the grid owners planned investment growth and in the order backlog of the equipment companies in our grid theme.
As we have discussed in the past, the renewable energy space experienced a significant bubble in 2020 and has since been deflating. Investors have fled the sector; even sustainability focused investors rarely allocate toward the energy transition these days. For many companies, very little growth is being priced in, which we believe is simply wrong. Growth will come and for the companies with competitive advantages, it will also be profitable.
FUND PERFORMANCE – ANOTHER GOOD MONTH OF STOCK PICKING
March was another solid month where the fund gained 5.0% (I USD) despite a relatively conservative net positioning below 50% for most of the month. With almost two thirds of the themes in profit and gains on both the long and the short side, it was another month of good stock picking.
The best performing theme, contributing 2.1% to NAV, was as mentioned “US Renewable Development” which consists of only two long positions currently, the leading renewable developers Nextera Energy (NEE) and AES. Both companies have advantages in scale, cost, customer relationships, pipeline, and execution that position them to be leaders in powering DCs. Their customers, hyperscalers and other large DC owners, promise their clients very high uptime, up to only 26.3 minutes of downtime annually, and any delays in construction are extremely expensive as the chips are costly and the profitability of a top-notch AI DC is very high. This implies that hyperscalers and other owners of large data centres will mainly work with the leading developers. Moreover, according to Morgan Stanley, the large DC owners’ willingness to pay for two years faster ‘time to power’, i.e. the time for bringing data centres online, is up to a 100% premium on normal power prices if the economic life of graphic processing units (GPU) are 6 years. If the economic life of GPUs are 10 years, which would be a stretch, the premium is still above 60%. We believe this promise well for NEE and AES’ pricing power going forward.
The "Grid" theme added to the NAV for the fifth month in a row. As described earlier, it has become our largest theme as we see strong structural demand while the market is relatively consolidated, with few competitors and high entry barriers in many of the sub-sectors. Of course, at one point the market will be saturated and the expanded industry capacity will overwhelm demand, but we believe this is still years into the future. We continue to add companies to this theme.
The “Wind” theme also did well in March, adding 1% to NAV. Most of the profit stem from Nordex (NDX1), which got a boost from its Q4 report which verified the backlog growth and margin improvement we expected. The company is working through its low margin legacy projects during 2024, and gradually, margins will get stronger. The company also confirmed its mid-term EBITDA target of 8%, which believe it is likely to achieve in 2025. Nordex and Vestas have seldom faced a better competitive situation as the main competitors Siemens Gamesa and GE Vernova (GEV) are, at least for now, not bidding on onshore projects in Europe and Latin America. This should vouch well for continued pricing power on new orders.
The wind turbine players are also likely to benefit from the coming boom in AI data centers. Although solar has a lower LCOE than wind, the latter has an advantage as it increases the value of the solar for clients that want as high clean energy mix as possible. AES is e.g. offering its DC clients a mix of solar, wind and batteries to generate up to 92% clean and reliable electricity. The remaining electricity will come from the grid, but AES will help structure offsetting virtual PPA that are geographic and time matched securing 100% clean electricity for the climate focused clients.
The “Solar” theme was largest losing theme in March, deducting 0.6% from NAV. We have significantly reduced both the net and the gross exposure of the theme over the last months, but the fund still holds Shoals (SHLS) as a top pick in utility scale solar, but also partly as a hedge against some of the short positions in the theme. SHLS declined by 13% in March, slightly underperforming the rest of the utility scale exposed stocks. The biggest loser in the theme was however Altus Power (AMPS), which is the largest solar developer in the Commercial & Industrial (C&I) market in the US. The stock fell 23% on the day it reported Q4 results below expectations, coupled with a 2024 forecast that implied lower returns on newer projects. The company introduced some new financial metrics which might have confused the market, leading to the implied lower profitability. However, we believe the company has guided conservatively and estimate profitability to remain solid. We are still optimistic to growth in the solar C&I market and believe AMPS is very well positioned with Blackstone as a financial backer in an industry where scale, experience and access to financing are key competitive advantages. We added to the position on earnings day and the stock is up by about 5% since the bottom.
Sincerely
Vidar Kalvoy & Joel Etzler
- Portföljförvaltare och grundare av fonden Coeli Renewable Opportunities.
- Mer än 15 års erfarenhet av investeringar från både publika och private equity-sidan.
- Förvaltat fonden Coeli Energy Transition sedan 2019.
- Spenderade sex år på Horizon Asset i London, en marknadsneutral hedgefond.
- Började arbeta tillsammans med Vidar Kalvoy 2012.
- Fem år inom Private Equity på Morgan Stanley.
- Startade sin investeringskarriär inom tekniksektorn på Sweden Robur i Stockholm 2006.
- Utbildad Civilingenjör från Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan.
- Portföljförvaltare och grundare av Coeli Renewable Opportunities-fonden.
- Förvaltat aktier inom energisektorn sedan 2006 och har mer än 20 års erfarenhet från portföljförvaltning och aktieanalys.
- Förvaltat fonden Coeli Energy Transition sedan 2019.
- Ansvarig för energiinvesteringarna på Horizon Asset i London under 9 år, en marknadsneutral hedgefond.
- Erfarenhet från energiinvesteringar på MKM Longboat i London och aktieanalys inom teknologisektorn i Frankfurt och Oslo.
- MBA från IESE i Barcelona och Civilekonom från Norges Handelshögskola.
- Innan han började arbeta inom finans var han löjtnant i norska marinen.
VIKTIG INFORMATION. Denna information är avsedd som marknadsföring. Fondens prospekt, faktablad och årsberättelse finns att tillgå på coeli.se och rekommenderas att läsas innan beslut att investera i den aktuella fonden. Prospektet och årsberättelsen finns på engelska och fondens faktablad finns bland annat på svenska och engelska. En sammanfattning av dina rättigheter som investerare i fonden finns tillgängligt på https://coeli.se/finansiell-och-legal-information/.
Historisk avkastning är ingen garanti för framtida avkastning. En investering i fonder kan både öka och minska i värde. Det är inte säkert att du får tillbaka det investerade kapitalet.
